Showing
- docs/dev/web/i18n.rst 109 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/dev/web/i18n.rst
- docs/dev/web/model.rst 153 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/dev/web/model.rst
- docs/dev/web/view.rst 60 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/dev/web/view.rst
- docs/features/autoupdater.rst 57 additions, 23 deletionsdocs/features/autoupdater.rst
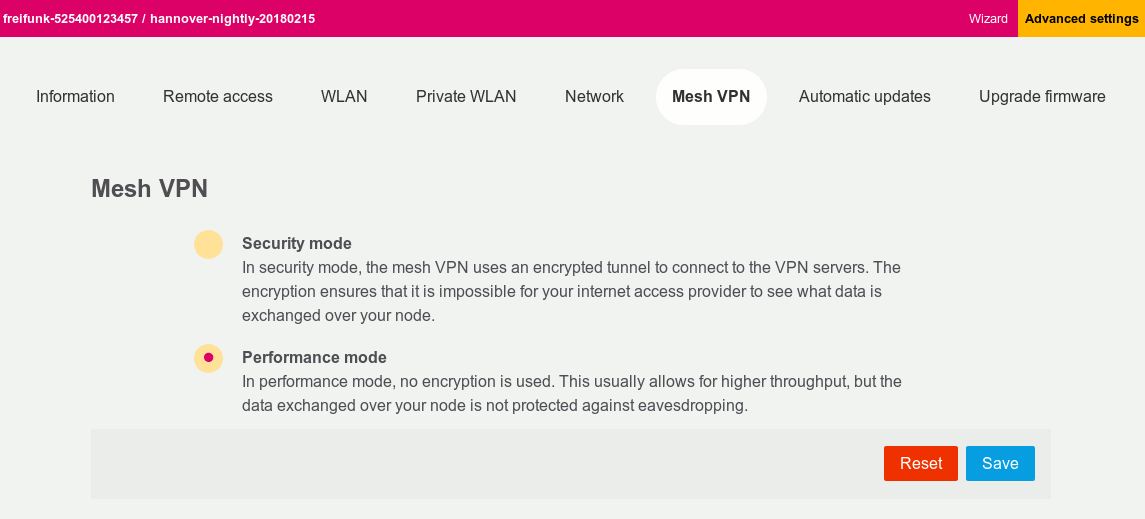
- docs/features/configmode.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/configmode.png
- docs/features/configmode.rst 19 additions, 2 deletionsdocs/features/configmode.rst
- docs/features/dns-cache.rst 53 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/dns-cache.rst
- docs/features/fastd_mode.gif 0 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/fastd_mode.gif
- docs/features/monitoring.rst 11 additions, 10 deletionsdocs/features/monitoring.rst
- docs/features/multidomain.rst 273 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/multidomain.rst
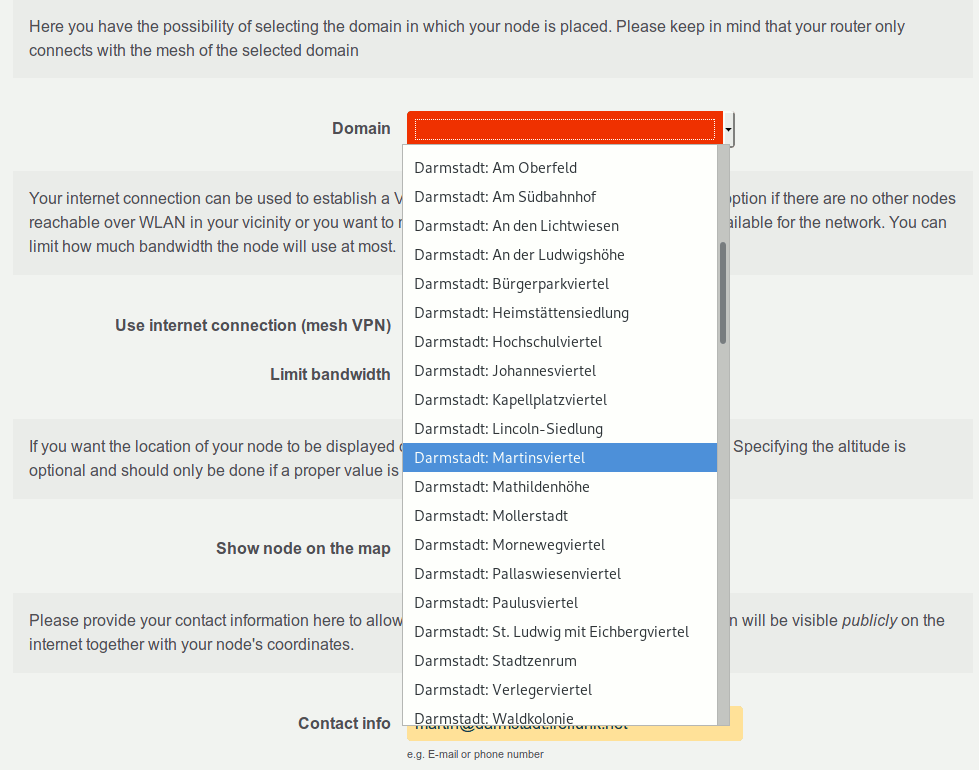
- docs/features/multidomain_configmode.gif 0 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/multidomain_configmode.gif
- docs/features/private-wlan.rst 24 additions, 11 deletionsdocs/features/private-wlan.rst
- docs/features/roles.rst 12 additions, 10 deletionsdocs/features/roles.rst
- docs/features/status-page.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/status-page.png
- docs/features/status-page.rst 30 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/status-page.rst
- docs/features/tls.rst 10 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/tls.rst
- docs/features/vpn.rst 250 additions, 0 deletionsdocs/features/vpn.rst
- docs/features/wired-mesh.rst 102 additions, 34 deletionsdocs/features/wired-mesh.rst
- docs/features/wlan-configuration.rst 16 additions, 17 deletionsdocs/features/wlan-configuration.rst
- docs/index.rst 70 additions, 229 deletionsdocs/index.rst
Some changes are not shown.
For a faster browsing experience, only 20 of 1000+ files are shown.
docs/dev/web/i18n.rst
0 → 100644
docs/dev/web/model.rst
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
docs/dev/web/view.rst
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
docs/features/configmode.png
0 → 100644
112 KiB
docs/features/dns-cache.rst
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
docs/features/fastd_mode.gif
0 → 100644
28.1 KiB
This diff is collapsed.
docs/features/multidomain.rst
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
docs/features/multidomain_configmode.gif
0 → 100644
57.1 KiB
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.
docs/features/status-page.png
0 → 100644
150 KiB
docs/features/status-page.rst
0 → 100644
docs/features/tls.rst
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
docs/features/vpn.rst
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.